Lateral Flow Test Pads have gained significant importance in rapid diagnostic applications, including detecting diseases and infections.
These tests rely on the use of specialized test pads that play a crucial role in the accurate and efficient functioning of the assay.
In this article, we will explore the components and functions of lateral flow test pads, shedding light on their significance in diagnostic testing.
Lateral flow strip cutter tests, also known as lateral flow assays or immunochromatographic assays, are widely used for rapid diagnostic testing.
These tests offer simplicity, speed, and ease of use. They are valuable tools in point-of-care settings, resource-limited environments, and mass screening programs.
Various components make up lateral flow test pads, which form the backbone of these tests and enable the detection and interpretation of target analytes.
Components of Lateral Flow Test Pads
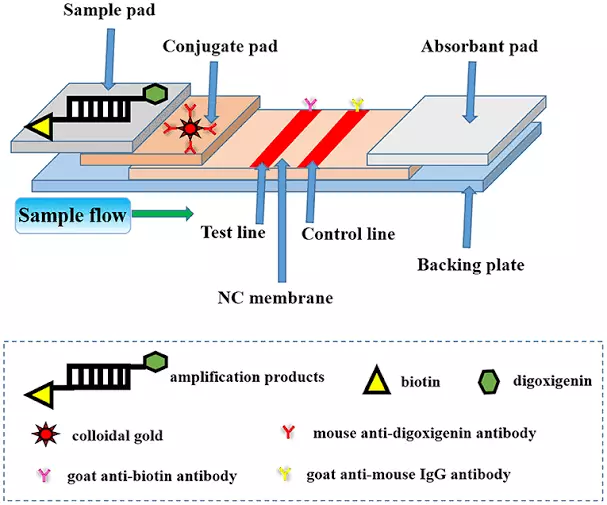
Lateral flow test pads typically consist of four essential components:
- Sample Pad
- Conjugate Pad
- Nitrocellulose Membrane
- Absorbent Pad
Each component serves a specific function in the lateral flow assay, contributing to the overall performance and accuracy of the test.
Sample Pad
The sample pad is the initial point of contact for the test sample, which can be a biological fluid such as blood, urine, or saliva.
It acts as a filter, wicking the sample and facilitating its flow through the test strip. The sample pad is typically made of cellulose or glass fibers.
It is often treated with surfactants to enhance sample migration and promote uniform distribution of the target analyte.
Conjugate Pad
The conjugate pad, also known as the reagent or test line pad, contains conjugated particles or molecules specific to the target analyte.
These particles or molecules are typically labeled with a marker, such as colloidal gold nanoparticles or fluorescent dyes, enabling the target analyte’s detection.
The conjugate pad acts as a reservoir of labeled reagents. They interact with the sample and migrate through the test strip.
Nitrocellulose Membrane
The nitrocellulose membrane, also called the test strip or the nitrocellulose strip, is a critical component of lateral flow tests.
It consists of a porous membrane that contains immobilized capture molecules, typically antibodies or antigens specific to the target analyte.
The nitrocellulose membrane serves as a detection zone, allowing the interaction between the labeled conjugates from the conjugate pad and the target analyte from the sample.
The nitrocellulose membrane is structured to create specific zones, including the test line and the control line. The test line contains immobilized capture molecules that capture and bind to the target analyte or its particular antibodies.
This results in a visible signal (such as a colored line) when the test is positive. The control line also contains immobilized molecules.
It reacts with the labeled conjugate, ensuring the test’s proper functioning and validating its correctness.
Absorbent Pad
The absorbent pad, also known as the waste pad or porous membrane, is located at the end of the lateral flow test strip.
It functions as a reservoir for excess fluid, aiding in the capillary flow of the sample and labeled conjugates through the test strip.
The absorbent pad helps maintain the flow rate, prevents backward flow, separates unreacted components, and generates a transparent and interpretable test result.
Functions of Lateral Flow Test Pads
The components of lateral flow test pads work together to perform several crucial functions, including:
- Sample filtration and wicking: The sample pad filters the test sample and facilitates its migration through the test strip via capillary action.
- Sample and conjugate interaction: The conjugate pad contains labeled reagents that specifically interact with the target analyte present in the sample.
- Target analyte capture: The nitrocellulose membrane captures and immobilizes the target analyte or its specific antibodies at the test line, enabling its detection.
- Signal generation and interpretation: The presence of the target analyte is indicated by a visible signal, such as a colored line, at the test line. The control line validates the test’s proper functioning.
- Fluid management and waste collection: The absorbent pad ensures the proper flow rate of the sample and labeled conjugates and collects excess fluid, preventing backward flow and contamination.
The coordinated functioning of these components ensures the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of lateral flow tests. Allowing for rapid and convenient diagnostic testing.
Conclusion
Lateral flow strip cutter test pads play a critical role in the performance and accuracy of lateral flow assays.
The sample pad, conjugate pad, nitrocellulose membrane, and absorbent pad work together to facilitate sample migration, promote target analyte interaction, and capture.
And detect the target analyte, generate visible signals, and manage fluid flow. Understanding the components and functions of lateral flow test.
Pads are essential for successfully designing and implementing diagnostic tests, enabling effective and reliable detection of target analytes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can lateral flow test pads be customized for different analytes or applications?
Yes, it can be tailored to specific analytes and applications by selecting appropriate capture molecules, labeled conjugates, and membrane configurations.
Q2. Are lateral flow test pads reusable?
Lateral flow test pads are typically designed for single-use applications and are disposable. Reusing test pads may lead to contamination and inaccurate test results.
Q3. Can lateral flow test pads be stored for an extended period?
It should be stored according to the manufacturer’s instructions, typically in a cool and dry place. Improper storage conditions may impact the test pads’ performance and reliability.
Q4. Do lateral flow test pads require specialized equipment for interpretation?
Lateral flow tests are designed for visual interpretation, and the results can be read with the naked eye. However, in some cases, specialized readers or scanners may be used for quantitative analysis or to enhance the accuracy of the results.
Q5. Can lateral flow test pads be used for multiple analytes in a single test?
It can be customized to incorporate multiple test lines. Allowing for the detection of various analytes in a single test strip. This capability is precious in multiplex testing scenarios.