Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a popular communication technology used to make and receive voice calls over the Internet. Radio over Internet protocol or RoIP refers to a similar technology that allows radio communications over the Internet. Both technologies have interfaces that work on mobile phones, computers, radio phones, and other devices. Here’s an overview of the main differences between voice and radio over IP communications and devices:
What Is VoIP?
VoIP lets users make voice calls using an internet connection instead of analog phone lines. Each VoIP service is unique, so some only allow calls using the same service. Other services accommodate calls to anyone with a telephone number so that you can reach local, long-distance, and international numbers.
VoIP converts voice into digital signals transmitted over the Internet to the destination. The technology allows users to call from a VoIP phone, computer, or traditional phone with a special VoIP adapter. You can also use VoIP services wirelessly through wireless hotspots in some airports, cafes, and parks.
Read More: Blooket Login
What Is RoIP?
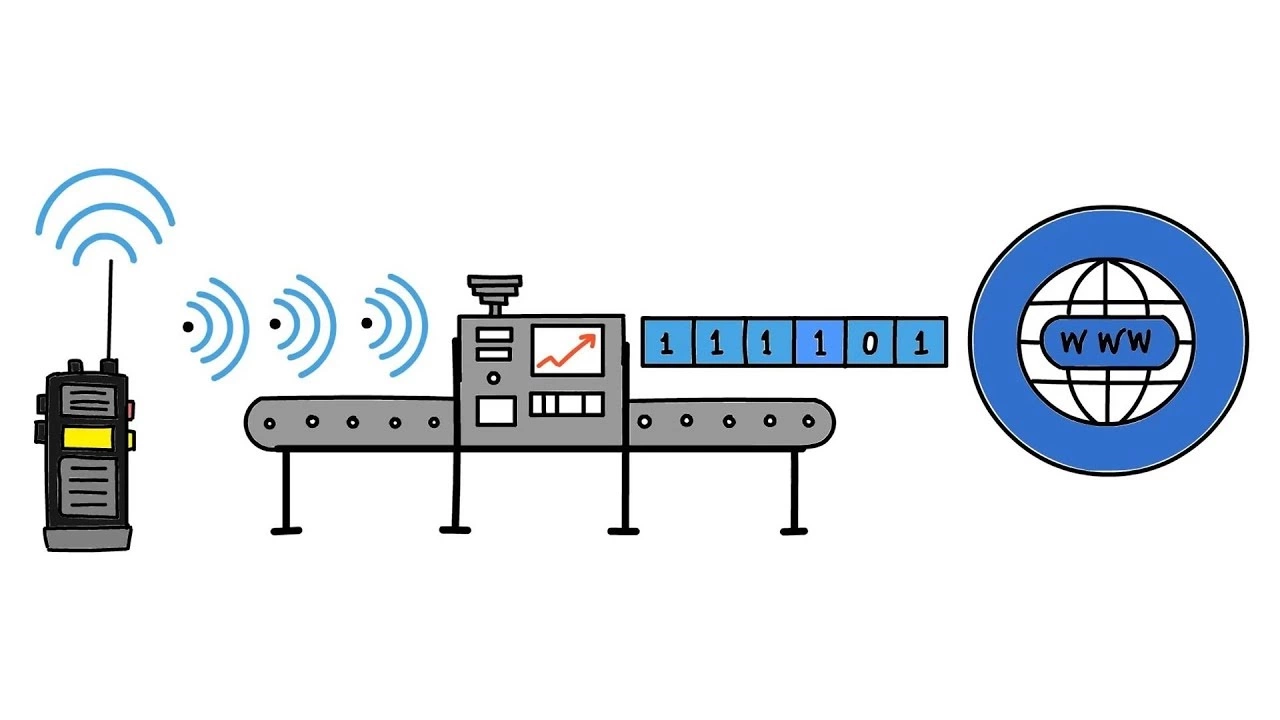
Radio over IP shares a lot with Voice over IP but offers radio communication capabilities. The technology transmits in a half-duplex, so only a single device communicates simultaneously. Users press the push-to-talk (PTT) button each time to speak. The also includes receivers that convert digital signals to analog at both ends.
Receivers convert analog radio signals to digital signals transmitted through the internet backbone. They also convert digital signals back to analog at the receiving end. RoIP allows users to connect two or more radio sites and allows communications between networks with non-compatible hardware and architecture.
How Are They Different?
Voice and radio over IP s are similar because they use Internet protocol standards to transmit audio signals. The primary distinction is that radio over IP uses push-to-talk.
In voice-over IP s, users can talk simultaneously without pushing a button. This fundamental difference also means voice and radio over IP users vary. Here are two main differences between the two communications s:
Unique Hardware & Software
Voice-over IP s require a high-speed internet connection, a computer, an adaptor, and a specialized phone (optional). You’ll need software and an external microphone if you use the service on your computer. VoIP phones can connect directly to your broadband connection like traditional phones. Systems with a conventional telephone also need a VoIP adapter.
RoIP s involve portable radios with PTT, a computer, a gateway, and a digital-to-analog receiver. Users push the PTT button to talk into the portable radio. The computer picks up the voice signal and converts it to a radio wave transmitted to the gateway. Radio over IP gateway is the solution that connects multiple radio s over different networks.
Different Applications & User Bases
Although VoIP and RoIP share the same technology, they have different applications. The military, utility companies, emergency operators, and public safety departments commonly use radio over IP services. VoIP is available for a more extensive user base. Anyone looking for enhanced communication performance can use a VoIP .
VoIP works efficiently for basic audio communications but is limited, especially when transferring radio and console signals. The ‘s infrastructure isn’t built for audio transmissions requiring carrier-operated relay (COR) and PTT communications. RoIP s are designed specifically for applications with such specifications.
Key Takeaways About Voice and Radio Over IP
VoIP and RoIP are communication technologies that transmit audio signals using the internet protocol standard. Radio over IP is similar to voice over IP, except for the addition of PTT and COR capabilities. This distinction also causes differences in hardware, software, user base, and application. Some providers offer both voice and radio services and fax, video, and data communications. Others focus on providing either voice or radio over IP services.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Difference Between VOIP and ROIP
A1: VOIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a technology that enables voice communication and multimedia sessions over the Internet. It converts analog audio signals into digital data. Allowing for voice calls using an internet connection.
A2: ROIP, or Radio over Internet Protocol, is a that extends the reach of radio communication by integrating it with Internet protocols. It connects traditional radio s to the Internet, enabling communication over long distances through various networks.
A3: VOIP primarily focuses on voice communication over the internet, supporting real-time conversations. On the other hand, ROIP is specialized for radio communication, linking radio networks through IP networks, extending coverage, and facilitating communication between different radio s.
A4: VOIP is commonly used for voice calls, video conferencing, and multimedia communication over the Internet. It’s prent in business environments, offering cost-effective and flexible communication solutions.
A5: ROIP is crucial in scenarios where radio communication needs to extend beyond local networks. It’s employed in public safety, transportation, and industries relying on radio s. Enabling seamless communication across diverse geographical locations.
A6: Yes, VOIP can be integrated with traditional phone s. Allowing businesses to leverage internet-based communication while retaining compatibility with existing infrastructure. This integration enhances flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
A7: ROIP enhances radio communication by connecting radio s to the internet. It facilitates interoperability between different radio networks. Enabling efficient communication between diverse radio devices and users.
While VOIP is tailored for internet-based voice communication, ROIP specializes in extending the reach of radio s through internet protocols, enhancing communication capabilities in various industries.